Sustainability in building design and construction has gained momentum over the past few decades, and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is at the forefront of this movement. If you’re new to the world of sustainable building or simply curious about how modern buildings are designed with the environment in mind, this post will walk you through the basics of LEED, what it stands for, and why it’s important.
Interior Design X Green Design
Over the years, I have come to realize that my job is more than just making places look cool (I am a designer, BTW). And, yes, I do make places look really cool. But, like I said, design, well at least GOOD design, is more than just aesthetic. I believe it’s the responsibility of everyone in the interior design, construction, and building development industries to make environmentally conscious decisions. Building green might not be the easiest endeavour, or the most cost-effective, however it is the right thing to do. And there is a saying; the hard thing and the right thing are often the same thing.

LEED for dummies
LEED is a globally recognized green building certification system. Green Building Council (USGBC), rates the sustainability and environmental impact of buildings. LEED-certified buildings are designed to be healthier for occupants, use fewer resources, and emit fewer pollutants.
Buildings earn LEED certification by accumulating points in various categories, which measure their eco-friendliness. LEED can apply to all building types, including commercial, residential, schools, healthcare facilities, and even entire neighbourhoods.
The LEED Certification Levels
LEED operates on a point system, where buildings can achieve different levels of certification based on how many points they earn. These levels are:
- Certified: 40-49 points
- Silver: 50-59 points
- Gold: 60-79 points
- Platinum: 80+ points
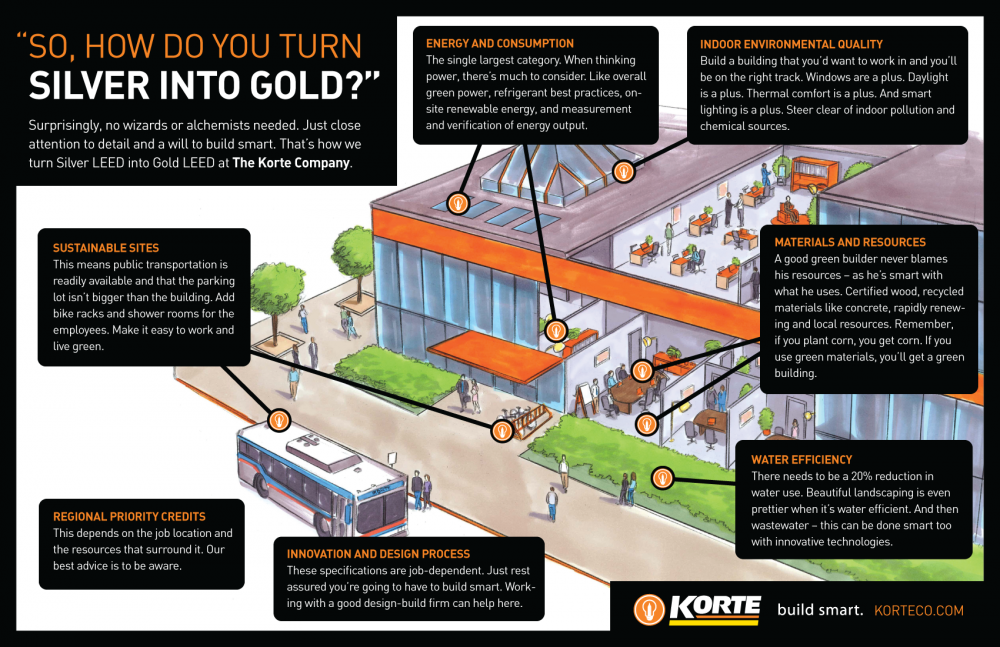
Points are awarded based on performance in specific key areas. Including; energy efficiency, water conservation, material selection, and indoor environmental quality. The more points a building earns, the higher its certification level.

Categories
Buildings earn LEED points across several categories. Here’s a brief look at each:
- Location & Transportation: This evaluates the building’s location, access to public transport, and its effect on reducing transportation-related carbon emissions.
- Sustainable Sites: Focuses on the impact of the site itself, encouraging minimal environmental disruption, efficient use of land, and integration with natural surroundings.
- Water Efficiency: Addresses water conservation, promoting strategies like low-flow plumbing and water-efficient landscaping.
- Energy & Atmosphere: Perhaps the most impactful category, it encourages energy-efficient design, renewable energy use, and greenhouse gas reduction.
- Materials & Resources: This category pushes for sustainable sourcing of building materials, recycling, and reducing waste during construction.
- Indoor Environmental Quality: Evaluates factors like air quality, natural light, and ventilation, all of which directly affect the well-being of building occupants.
- Innovation: Allows for creative strategies that go beyond traditional sustainability measures.
- Regional Priority: Rewards projects for addressing local environmental priorities.
The Benefits
- Environmental Benefits: LEED buildings are designed to reduce energy and water use, decrease waste, and minimize the building’s overall carbon footprint. By integrating renewable energy and resource conservation, these buildings help fight climate change.
- Economic Savings: While achieving LEED certification may have an upfront cost, the long-term financial benefits include lower utility bills, reduced operating costs, and potentially higher property values.
- Healthier Spaces: LEED-certified buildings prioritize indoor air quality, natural lighting, and reduced exposure to harmful chemicals, leading to healthier living and working environments.
- Market Value: LEED certification can make buildings more attractive to buyers, tenants, and investors who are interested in sustainable living.
LEED for the Studious
For building owners, designers, architects, and developers looking to certify a project, the first step is understanding the LEED rating system and working with LEED Accredited Professionals to ensure the design and construction align with the certification criteria.
If you’re an individual looking to make a difference in green building, you can become a LEED Green Associate or a LEED Accredited Professional by passing an exam. These credentials demonstrate your knowledge of green building practices and your commitment to sustainability.
Currently, I am planning on taking the LEED Green Associate exam! I have some more studying to do. However, it is the next certification I want to pursue.
Healthy Buildings = Healthy People
LEED is not just about reducing a building’s carbon footprint. It’s about creating spaces that benefit both the environment and the people who inhabit them. As sustainability becomes increasingly crucial, LEED provides a clear, measurable way to ensure that buildings are doing their part in the fight for a greener future.
Whether you’re a building owner, designer, architect, or someone passionate about environmental responsibility, LEED is a key tool in transforming the built environment for the better.
Read A Simple Guide to Eco-Friendly Interior Design.
Click Here To Shop My Favourite Home Goods
Let’s design your space together, virtually.



